New Jersey Route 52 Bridge Hydrologic & Hydraulic Analyses
« Return to Project SearchAyres performed tidal hydraulic, scour, and stability analyses for the proposed Route 52 bridge replacement over Great Egg Harbor Bay.
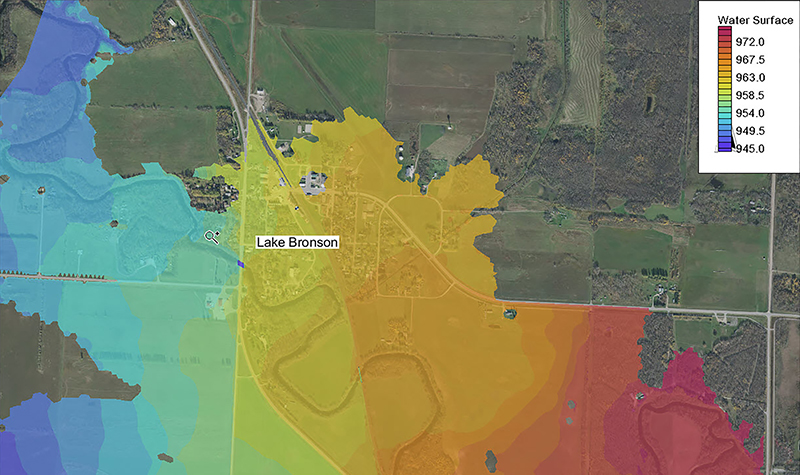
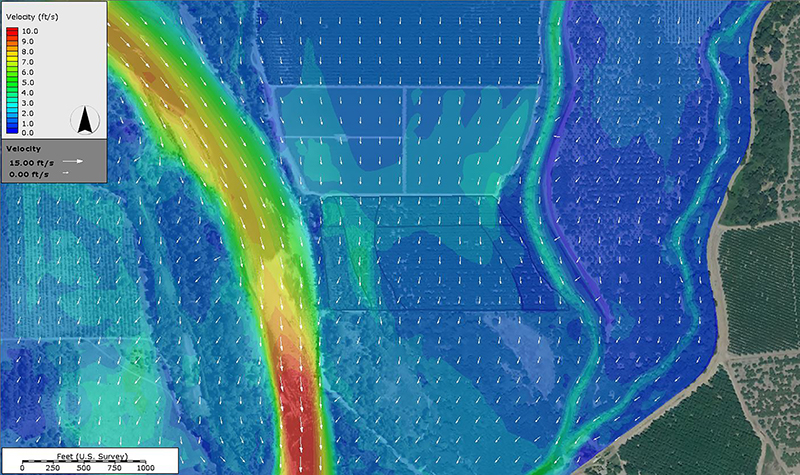
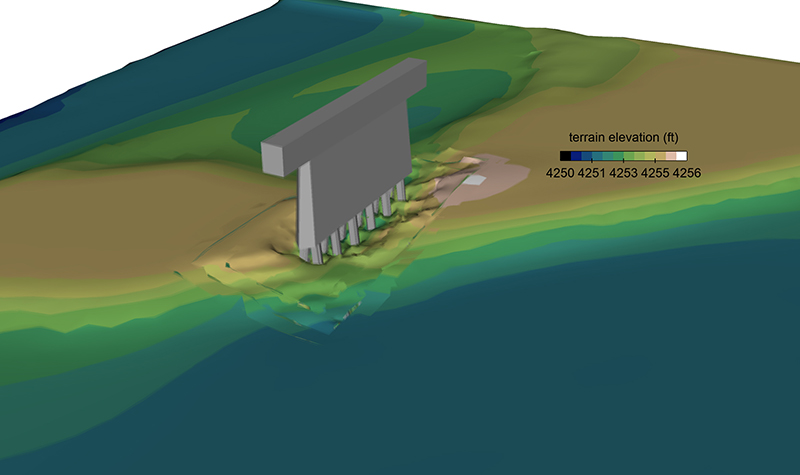
The modeling determined design discharge rates, water surface elevation, flow depths, and flow velocities along the proposed bridge alignment. Scour analyses were performed for the 100- and 500-year storm tide events. Long-term lateral and vertical stability trends were assessed.
The analyses included storm tide development; 2-dimensional hydrodynamic modeling using RMA-2V; 2-dimensional wave climate analysis using STWAVE; 1-dimensional modeling using HEC-RAS; and scour analyses in accordance with FHWA guidelines in HEC-18 and HEC-20. Rock riprap countermeasures were designed using methods outlined in HEC-23 and the Shore Protection Manual.
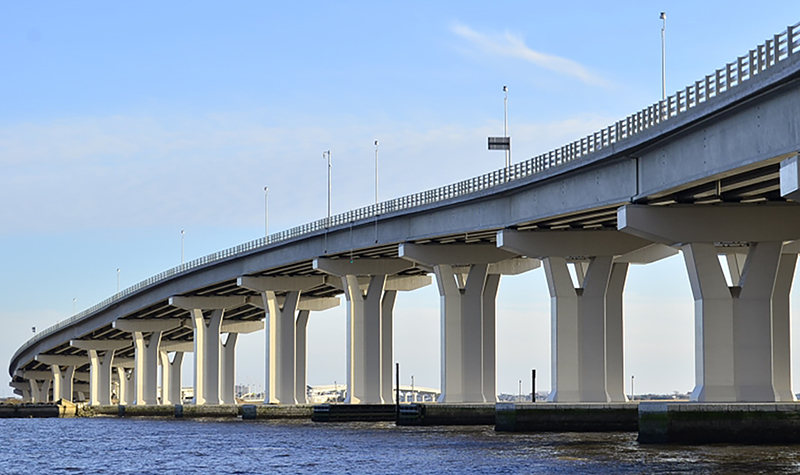
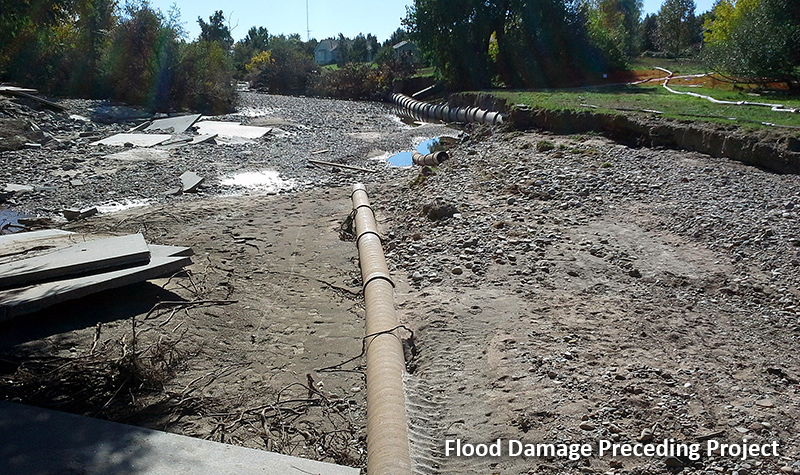
The Route 52 Causeway crosses the Great Egg Harbor near its inlet. The previous causeway had four bridge openings separated by embankment segments. Several tidal marsh islands exist in the vicinity. A network of tidal channels of varying widths and depths separates the islands. Tidal processes dominate the hydraulics in the vicinity of the causeway. Storm surges cause the most severe hydraulic conditions in the bay.
Ayres’ work was performed in support of the replacement bridge design. The new crossing consists of two structures connected with a short segment of structural fill at Rainbow Island.
Project Information
Client's NameNew Jersey Department of Transportation
LocationCape May County and Atlantic County, NJ
Primary ServiceRiver Engineering + Water Resources
MarketState + Federal + Tribal